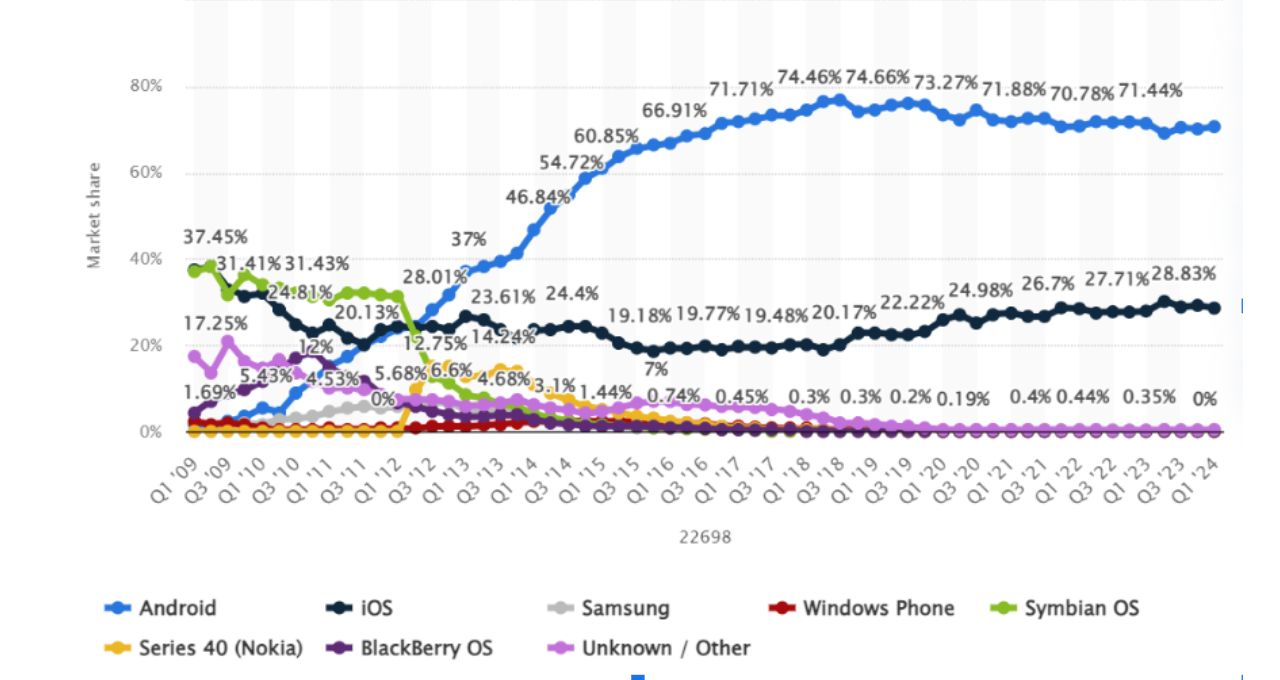
Did you know – Android maintained its position as the leading mobile operating system worldwide in the first quarter of 2024 with a market share of 70.7%? Android’s closest rival, Apple’s iOS, had a market share of 28.5% during the same period. (Statista)
What makes Android the leader because of its capability to adopt a different range of devices, such as Samsung, Google, Motorola, OnePlus, and many others. While the iOS only runs on Apple devices.
Since the inception of Google’s Android and Apple’s iOS, both have gained immense popularity, not just because of their interface and ease of use but their incremental updates which included new features and capabilities introduction.
We are already aware that iOS released iOS 17 in September 2023 and Android released Android 14 in October’23. Regardless of these releases, only 66% of the iOS users installed the latest version, and only 13% of the Android users ran the latest version.
How has the new iOS operating system upgraded and improved since its inception? Let’s find out!
iOS From Inception to Now
Apple’s iOS operating system has undergone significant improvements since its inception in 2007. Here’s a breakdown of how new iOS versions are typically upgraded and how they offer advancements over previous versions:
The Upgrade Process:
Over-the-Air Updates (OTA):
Starting with iOS 5 in 2011, Apple has primarily used OTA updates. This allows users to download and install the latest version directly on their iPhones or iPads through a Wi-Fi connection. It’s a convenient and user-friendly process.
Backup and Restore:
It’s recommended to back up your device before installing a major update. This ensures you can restore your data in case of any issues.
Gradual Rollout:
Apple often implements a staged rollout process for major iOS updates. This allows them to identify and fix any potential problems before the update becomes available to everyone.
Improvements Over Time:
Here are some key areas where iOS has improved significantly since its inception:
Performance:
Newer iOS versions are generally faster, smoother, and more efficient than older ones. This is due to advancements in hardware and software optimization.
Security:
Apple prioritizes security with each new iOS update. These updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities discovered in previous versions.
Features:
New features are constantly being added to iOS. These features can range from new multitasking functionalities to improved camera capabilities and integration with new Apple services.
Design:
The iOS design has evolved, becoming more visually refined and user-friendly with each iteration.
Accessibility:
Apple has made significant strides in improving accessibility features within iOS. These features cater to users with disabilities, ensuring everyone can use their devices effectively.
Here’s an example of specific improvements in the upcoming iOS 18:
Focus on AI:
iOS 18 is rumoured to introduce “Apple Intelligence,” a set of AI features designed to personalize the user experience and automate tasks.
Customizable Homescreen:
Users are allowed to freely place app icons and widgets anywhere on the screen, breaking away from the rigid grid layout.
Enhanced Apps:
Built-in apps like Maps and Settings are expected to receive updates with improved functionalities and organization.
Overall, Apple’s strategy of regular iOS updates ensures that iPhones and iPads stay up-to-date with the latest features, security patches, and performance improvements. This continuous evolution keeps iOS a leading mobile operating system.
Let’s move to Android and learn about the inception of this operating system and its improvements and upgrades ever since.
Android From Inception to Now
Upgrading and advancements in the Android operating system follow a distinct path compared to Apple’s iOS. Here’s a breakdown of the Android update process and how it has improved since its debut in 2008:
The Upgrade Process:
Manufacturer Dependency:
Unlike iOS with a single source (Apple), Android updates are distributed by device manufacturers and carriers, leading to fragmentation.
Over-the-Air Updates (OTA):
Similar to iOS, most modern Android devices receive OTA updates directly over Wi-Fi.
Varied Rollout Times:
Due to manufacturer customization and carrier testing, the latest Android version might not reach all devices simultaneously. This can lead to frustration for users with older devices.
Improvements Over Time:
Despite the fragmentation challenge, Android has come a long way since its launch:
Performance:
Newer Android versions are generally faster and smoother due to hardware advancements and software optimizations by Google.
Security:
Google releases regular security patches to address vulnerabilities. However, patch rollout depends on manufacturers and carriers, impacting security for some users.
Features:
New features are introduced with each iteration, ranging from improved multitasking to enhanced notifications and privacy controls.
Openness and Customization:
Android remains an open-source platform, allowing manufacturers to customize the look and feel (sometimes adding bloatware). Users with compatible devices can also flash custom ROMs for even greater control.
Google Play Services:
This suite of apps and APIs (like Google Maps) constantly evolves, adding new functionalities to the Android experience.
Here’s an example of improvements in the upcoming Android 14:
Focus on Multitasking:
Android 14 might introduce better multitasking features like split-screen improvements and a taskbar for easier app switching.
Enhanced Privacy:
New privacy features are rumoured, giving users more granular control over app permissions and data access.
Material You 3:
The design language, Material You, might see further refinement, offering users more customization options for their device’s look and feel.
Overall, Android prioritizes openness and flexibility. This allows for faster innovation but can lead to fragmentation and slower update rollouts. Google works to improve the update process, and some manufacturers are becoming more prompt in delivering the latest versions. However, fragmentation remains a challenge for the Android ecosystem.
A quick differentiation between the iOS and Android operating systems will help you handpick the perfect OS for your needs. By connecting with the right company among mobile app development companies, you can develop a perfect app for your business.
Differentiating Android vs iOS

| Feature/Aspect | iOS | Android |
| User Interface | Simple, consistent design across all Apple devices | Varies by manufacturer; customizable with different skins and launchers |
| Ease of Use | Intuitive, user-friendly, and consistent across devices | May have a learning curve due to diverse interfaces and settings |
| App Store | Apple App Store; strict quality control ensuring high standards | Google Play Store; larger app selection but with more variability in quality |
| Customization | Limited to changing wallpapers, app icons, and arranging apps | Extensive customization including home screen widgets, third-party launchers, and system-wide themes |
| Voice Assistant | Siri, integrated deeply into the system and Apple services | Google Assistant, is generally considered more powerful and versatile with wider third-party integration |
| Hardware Variety | Limited to Apple devices (iPhone models) | Wide range of devices from various manufacturers (Samsung, Google, OnePlus, etc.) catering to different budgets |
| Integration with Ecosystem | Excellent integration with other Apple products (Mac, iPad, Apple Watch, iCloud) | Strong integration with Google services (Gmail, Google Drive, Google Photos); can vary with other ecosystems (Samsung Galaxy ecosystem) |
| Software Updates | Regular, timely updates for all compatible devices, often for several years | Updates depend on the manufacturer and carrier; flagship devices receive updates faster than budget models |
| Security | Strong emphasis on security and privacy; regular updates and strict app store policies | Security varies by manufacturer; Google Play Protect helps, but overall security can be inconsistent |
| Pre-installed Apps | Minimal bloatware, mainly essential apps from Apple | Varies widely; often includes additional apps from manufacturers and carriers, which can be considered bloatware |
| Price Range | Generally premium pricing; iPhone SE offers a more affordable entry point | Wide range from very affordable budget devices to premium flagship models |
| Customer Support | Strong support through Apple Stores, official website, and customer service | Varies by manufacturer; top brands offer good support, but can be inconsistent for lesser-known brands |
| Learning Curve | Easier for new users due to simplicity and uniformity across devices | Can be steep for new users due to varying interfaces and extensive customization options |
| Third-Party App Support | High-quality apps due to stringent guidelines; optimized for performance | More third-party apps available; quality can vary significantly, with more risk of encountering lower-quality or malicious apps |
| Battery Management | Generally good battery optimization; battery health management features | Battery performance varies by device; some manufacturers offer extensive battery optimization settings |
| Voice and Accessibility Features | Robust set of accessibility features like VoiceOver, AssistiveTouch, and hearing aid compatibility | Extensive accessibility features including TalkBack, magnification, and customizable display settings; vary by manufacturer |
| Cloud Services | iCloud for seamless syncing and storage across Apple devices | Google Drive, Google Photos, and other services; strong integration with the Google ecosystem |
| App Compatibility | Apps are generally optimized for performance and uniform experience across devices | Compatibility can vary; some apps may perform differently depending on the device and manufacturer |
| User Community and Support Forums | Active user community and official Apple support forums | Large and diverse user community; active forums and support from both Google and device manufacturers |
This table provides a detailed comparison of iOS and Android, covering various factors that new smartphone users might consider when choosing between the two operating systems.
Choosing Your Mobile Match: Final Thoughts on iOS vs. Android

So, iOS or Android? The answer truly depends on your priorities as a new smartphone user. Here’s a quick recap:
iOS:
Strengths:
User-friendly interface, seamless updates, tight integration with Apple ecosystem, strong security focus.
Considerations:
Limited customization, generally higher hardware costs.
Android:
Strengths:
Openness and flexibility, wider range of device options at various price points, faster innovation in some areas.
Considerations:
Fragmentation can lead to slower updates and potential security concerns, some interfaces can be more complex for beginners.
Ultimately, the best platform is the one that best suits your needs and preferences. If you value simplicity, security, and a seamless user experience, iOS might be the ideal choice. If you crave customization, a wider budget range, and are open to exploring different interfaces, Android could be your perfect match.
No matter your choice, both iOS and Android offer powerful and user-friendly mobile experiences. With a little research and this guide as a starting point, you’re well on your way to selecting the smartphone that perfectly complements your digital life!